This is part 9 of HTML Form series. You can read previous parts here. In this part you will learn about input type url and input type search control.
input type=”url”
The <input> element of type “url” creates an input filed which enables user to enter the URL.
The <input type="url"> defines a field for entering a URL.
The input value is automatically validated to ensure that it’s either empty or a properly-formatted URL before the form can be submitted.
Example
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>input type="url"</title>
</head>
<body>
<form>
<label>Enter your website URL: </label>
<input type="url" name="website" placeholder="http://example.com"><br>
<input type="submit" value="send data">
</form>
</body>
</html>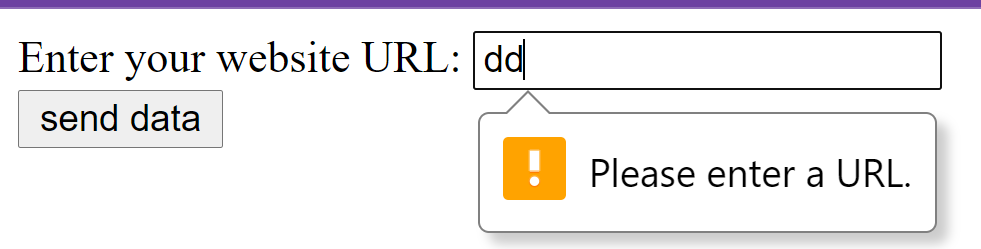
input type=”search”
The <input> type “search” creates an input filed which allows a user to enter a search string like a site search, or Google search. It is functionally symmetrical to the text input type, but may be styled differently.
It is required to set a name for the search field, otherwise nothing will be submitted. The most common name for search inputs is q.
The <input type="search"> defines a text field for entering a search string.
Example
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>input type="search"</title>
</head>
<body>
<form>
<label>Search here:</label>
<input type="search" name="q">
<input type="submit" value="search">
</form>
</body>
</html>