Variables are containers for storing data values. It saves the data values during Java program execution. It is the basic unit of storage in a program.
Every variable is assigned a data type that designates the type and quantity of value it can hold.
Variable is a memory location name of the data.
A variable is assigned with a data type.
A variable is a name given to a memory location.
The value stored in a variable can be changed during program execution. It is a combination of “vary + able” which means its value can be changed.
In Java, all the variables must be declared before use.
A variable is the name of a reserved area allocated in memory.
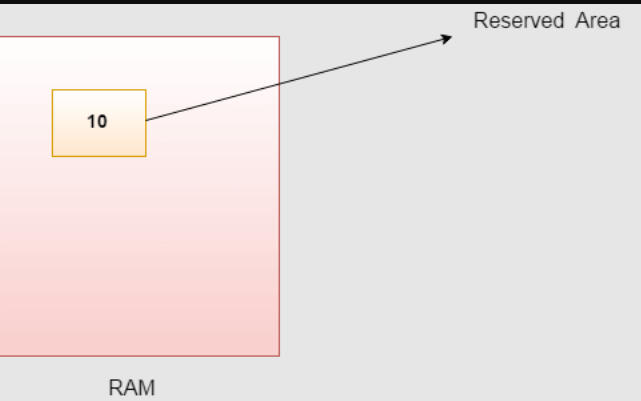
How to declare variables?
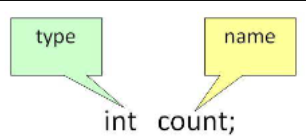
Datatype: Type of data that can be stored in this variable.
DataName: Name given to the variable.
How to initialize variables?
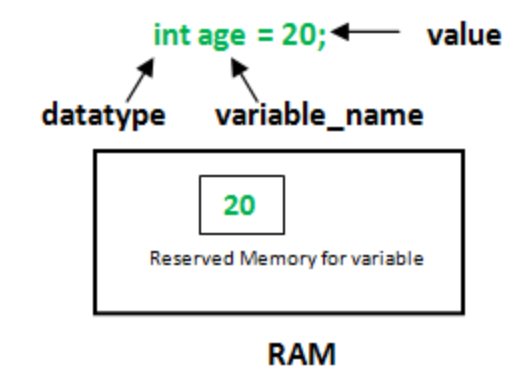
Examples
float simpleInterest;
// Declaring float variable
int time = 10, speed = 20;
// Declaring and Initializing integer variable
char var = 'h';
// Declaring and Initializing character variable